
🚀 Traditional IRA vs. Roth IRA and Other IRA Options: Which Retirement Account Is Right for You? 💰 Your Definitive E-E-A-T Guide
🔑 Section 1: Establishing E-E-A-T for Your Retirement Future
Navigating the landscape of Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) is a critical “Your Money or Your Life” (YMYL) decision. It directly impacts your financial stability, future security, and tax obligations for decades to come. Understanding the nuances of Traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs, and other options like SEP and SIMPLE IRAs requires a high degree of Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T).
At Sun Insurance & Financial, we embody these principles. Our Expertise comes from years of guiding Californians through complex financial decisions, helping them strategically plan for a secure retirement. This article is crafted to be your ultimate, Authoritative resource, providing accurate, honest, and actionable information you can Trust.
H3.1: Why Our Expertise Matters for Your IRA Decisions
Our licensed financial professionals have extensive Experience in:
- Analyzing individual income, tax situations, and retirement goals.
- Explaining complex IRS rules and contribution limits.
- Advising on optimal IRA strategies, including Roth conversions and tax-efficient distributions.
- Assisting small business owners with SEP and SIMPLE IRA setup.
We are experts in providing Californians’ insurance needs, and this dedication extends to robust retirement planning, recognizing the unique tax and economic environment of our state. Your financial future is too important for generic advice.
Ready to build a smart retirement strategy tailored for you?
To get a free consultation on your IRA options, Visithttps://SunInsurance.us/ira-individual-retirement-accountor call (310) 860-5000.
💡 Section 2: The Foundations of IRAs – What Are They?
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) are investment accounts that offer tax advantages to help individuals save for retirement.1 Unlike employer-sponsored plans like a 401(k), IRAs are individual accounts that anyone with earned income can open, regardless of their employment status.2 They are established with a financial institution (brokerage, bank, insurance company).
The “coverage” of an IRA isn’t about insurance payouts (though some financial products within an IRA, like annuities, might offer guarantees), but rather about its tax treatment and what investments it can hold.
H3.2: What an IRA “Covers” (Investment & Tax Advantages)
| Coverage Aspect | Description | E-E-A-T Implication (Clarity) |
| Investment Diversity | IRAs “cover” a vast array of investments: stocks 📈, bonds 📊, mutual funds, ETFs, CDs, real estate (through a self-directed IRA), and even annuities. This flexibility allows for broad portfolio diversification. | Expertise: Emphasizes the power of choice within an IRA, not just a savings account. |
| Tax-Advantaged Growth | The core “coverage” is tax deferral or tax-free growth. Investments grow without annual taxation on dividends or capital gains. This compounding effect is a major benefit for retirement savings. | Trustworthiness: Highlights a primary reason for IRA popularity. |
| Retirement Income | The ultimate “coverage” is a source of income in retirement. Depending on the IRA type, this income can be taxable or tax-free, offering flexibility for future needs. | User-Centric: Focuses on the end goal – financial security in retirement. |
| Penalty-Free Withdrawals | While designed for retirement, IRAs “cover” specific early withdrawals without penalty for certain qualifying events (e.g., first-time home purchase, qualified education expenses, disability). | Helpful Advice: Addresses common user questions about flexibility. |
H3.3: What an IRA Does NOT Cover (Limits & Guarantees)
It’s equally important to understand the limitations of an IRA:
- Not a Guarantee: An IRA is an account wrapper; it does not guarantee investment returns.3 The performance depends entirely on the underlying investments chosen.
- Contribution Limits: IRAs have annual contribution limits set by the IRS.4 You cannot contribute unlimited amounts.
- Income Limitations: For Roth IRAs, there are income phase-out limits that restrict who can contribute.5
- Early Withdrawal Penalties: While exceptions exist, taking money out before age 59½ for non-qualifying reasons typically incurs a 10% penalty plus ordinary income tax.6
- Health Insurance/Medical Costs: IRAs are for retirement savings; they do not cover healthcare costs directly (though funds can be used for medical expenses or premiums for unemployed individuals without penalty).7
Keywords for IRA Basics: #IRAExplained #RetirementAccounts #TaxAdvantagedSavings #InvestmentOptions #IRAContributions #IRSRules #RetirementPlanning101
⚖️ Section 3: The Big Decision – Traditional IRA vs. Roth IRA
This is often the central question for individuals saving for retirement: which IRA type offers the most benefit? The answer hinges on your current tax situation versus your expected future tax situation.
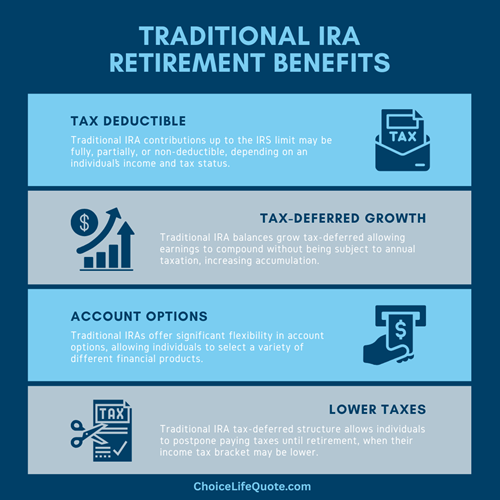
H3.4: Traditional IRA: Pre-Tax Contributions, Taxable Withdrawals 👵
The Traditional IRA is the elder statesman of individual retirement accounts. It’s often chosen by those who expect to be in a lower tax bracket in retirement than they are today.
Pros of a Traditional IRA: ✅
- Tax-Deductible Contributions: Contributions may be tax-deductible in the year they are made. This means you pay less in taxes now, reducing your current taxable income.
- Tax-Deferred Growth: Investments grow tax-deferred. You don’t pay taxes on dividends or capital gains until you withdraw the money in retirement.
- No Income Limit for Contributions: Anyone with earned income can contribute to a Traditional IRA, regardless of how much they earn (though deductibility may be limited for high-earners covered by an employer plan).8
- Potential for Catch-Up Contributions: If you are age 50 or older, you can contribute an additional “catch-up” amount annually.
- Qualified Distributions: Withdrawals after age 59½ are taxed as ordinary income, but for those in a lower retirement tax bracket, this can be very beneficial.

Cons of a Traditional IRA: ❌
- Taxable Withdrawals in Retirement: Every dollar you withdraw in retirement is taxed as ordinary income.9
- Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): You must start taking withdrawals by age 73 (or 72 if you turned 72 before 2023), even if you don’t need the money, or face a steep penalty.
- Deductibility Limitations: If you (or your spouse) are covered by a retirement plan at work and your income is above a certain threshold, your Traditional IRA contributions may not be fully tax-deductible.10
Who is a Traditional IRA Best For? 🎯
- Individuals who expect to be in a lower tax bracket in retirement than they are now.
- Those who want an immediate tax deduction to lower their current taxable income.
- High-income earners who want to contribute to an IRA but exceed Roth IRA income limits (they can make non-deductible contributions).
H3.5: Roth IRA: After-Tax Contributions, Tax-Free Withdrawals 👶
The Roth IRA is a newer option, highly popular for its incredible tax-free retirement income.11 It’s often chosen by those who expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement than they are today.
Pros of a Roth IRA: ✅
- Tax-Free Withdrawals in Retirement: Qualified withdrawals (after age 59½ and the account has been open for 5 years) are completely tax-free. This is its biggest advantage.
- Tax-Free Growth: Investments grow tax-free. You never pay taxes on the earnings, ever.
- No RMDs for Original Owner: The original owner of a Roth IRA is not subject to Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) during their lifetime, allowing for maximum tax-free growth and flexible withdrawal planning.12
- Access to Contributions Anytime, Tax-Free & Penalty-Free: You can withdraw your contributed principal at any time, for any reason, without tax or penalty. This offers a powerful emergency fund option.
- Catch-Up Contributions: Like Traditional IRAs, those age 50 or older can contribute an additional amount annually.
Cons of a Roth IRA: ❌
- No Upfront Tax Deduction: Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, so there’s no immediate tax break.13
- Income Limitations: There are income phase-out limits that restrict who can contribute directly to a Roth IRA.14 If your Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) is too high, you may not be eligible.
- Contribution Limits: Like Traditional IRAs, there are annual maximum contribution limits.15
Who is a Roth IRA Best For? 🎯
- Individuals who expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement than they are now.
- Younger workers in a lower tax bracket today, where the upfront tax deduction isn’t as valuable as future tax-free growth.
- Anyone who values tax-free income and flexibility in retirement, with no RMDs.
- High-income earners who are still eligible for a “Backdoor Roth” conversion.
Keywords for Traditional vs. Roth: #TraditionalIRA #RothIRA #TaxDeduction #TaxFreeRetirement #RMDs #AfterTaxContributions #PreTaxContributions #RothConversion #IRAComparison #FutureTaxBracket

📈 Section 4: Visualizing the Tax Impact – A Decision Framework
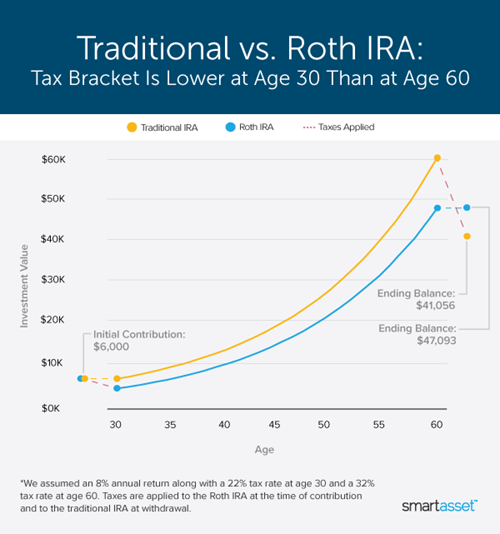
The choice between a Traditional and Roth IRA largely boils down to a bet on future tax rates. Let’s visualize this.
📊 Visual 1: Tax Impact of Traditional vs. Roth IRA 💰
This BAR CHART illustrates the difference in immediate tax savings vs. future tax-free growth.
| IRA Type | Contribution Today ($6,500) | Immediate Tax Impact (24% Bracket) | Future Tax Impact (on Growth) | Total Tax Benefit |
| Traditional IRA | Pre-tax | $-\$1,560$ (Immediate Tax Savings) | Taxable (Ordinary Income) | Tax deduction now, pay later. |
| Roth IRA | After-tax | $\$0$ (No Immediate Savings) | Tax-Free | Pay now, tax-free later. |
Interpretation:
- If you’re in a high tax bracket today and expect a lower one in retirement, a Traditional IRA’s upfront deduction is compelling.
- If you’re in a lower tax bracket today and expect a higher one in retirement, a Roth IRA’s future tax-free withdrawals are invaluable.
- E-E-A-T Advice: This decision requires personalized tax planning. We are experts in providing Californians’ insurance and financial needs, understanding that the state’s high-tax environment makes this choice particularly significant.
📉 Visual 2: The Power of Tax-Free Growth in a Roth IRA 🌟
This LINE GRAPH shows the compounding effect of tax-free growth, illustrating why a Roth IRA can be so powerful over decades.
| Year | Annual Contribution ($6,500) | Roth IRA Balance (7% Annual Return, Tax-Free) | Taxable Account Balance (7% Return, 24% Tax on Gains) |
| 10 | $65,000 | $94,930 | $90,120 |
| 20 | $130,000 | $267,090 | $240,110 |
| 30 | $195,000 | $614,030 | $528,780 |
Interpretation: Over 30 years, the Roth IRA balance is significantly higher due to the absence of taxes on annual gains. This differential becomes monumental over a long retirement horizon.
💡 Section 5: Other IRA Options – Beyond Traditional and Roth
While Traditional and Roth IRAs are for individuals, two other types of IRAs are specifically designed for small business owners and self-employed individuals: the SEP IRA and the SIMPLE IRA.16 These options demonstrate our comprehensive Expertise in supporting California’s diverse workforce.
H3.6: SEP IRA (Simplified Employee Pension) 💼
A SEP IRA is a retirement plan that allows self-employed individuals and small business owners to contribute to their own and their employees’ retirement accounts.17 Contributions are made solely by the employer (even if that’s you as a solo entrepreneur).
Pros of a SEP IRA: ✅
- High Contribution Limits: Significantly higher contribution limits than Traditional or Roth IRAs, allowing for substantial tax-deductible contributions.
- Simple to Set Up & Administer: Easy to establish and requires minimal paperwork compared to a 401(k).
- Flexible Contributions: You’re not required to contribute every year, and you can vary the contribution amount based on your business’s profitability.
- Tax-Deductible Contributions: All employer contributions are tax-deductible for the business.
- Tax-Deferred Growth: Investments grow tax-deferred until withdrawal in retirement.18
Cons of a SEP IRA: ❌
- Only Employer Contributions: Employees cannot contribute their own money.
- Non-Discriminatory Rule: If you contribute for yourself, you must contribute a proportional percentage for all eligible employees. This can be expensive for businesses with many employees.
- Withdrawals Taxed as Ordinary Income: Like a Traditional IRA, withdrawals in retirement are taxed.
Who is a SEP IRA Best For? 🎯
- Self-employed individuals (freelancers, independent contractors) or small business owners with few (or no) employees who want to contribute large amounts to their retirement.
- Businesses with fluctuating income, valuing contribution flexibility.
H3.7: SIMPLE IRA (Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees) 🤝
A SIMPLE IRA is another retirement plan for small businesses, often seen as a step between a SEP IRA and a full 401(k).19 It allows both employer and employee contributions.
Pros of a SIMPLE IRA: ✅
- Both Employer & Employee Contributions: Employees can contribute via salary deferral (pre-tax), and employers must either match employee contributions or make a non-elective contribution.
- Moderate Contribution Limits: Higher limits than Traditional/Roth IRAs, but lower than SEP IRAs.
- Relatively Simple Administration: Easier and less expensive to administer than a 401(k).
- Tax-Deductible Contributions: Employer contributions are deductible for the business, and employee contributions reduce their taxable income.
- Tax-Deferred Growth: Investments grow tax-deferred.
Cons of a SIMPLE IRA: ❌
- Mandatory Employer Contributions: Employers are legally required to make either a matching or non-elective contribution, regardless of business profitability.20
- Exclusive Plan: Generally, businesses cannot have another retirement plan (like a 401(k)) simultaneously.
- Early Withdrawal Penalty: A higher 25% penalty (instead of 10%) applies if funds are withdrawn within the first two years of participation.
Who is a SIMPLE IRA Best For? 🎯
- Small businesses (fewer than 100 employees) that want to offer a retirement plan to their employees without the complexity or cost of a 401(k).
- Businesses where both employers and employees want to contribute.
Keywords for Business IRAs: #SEPIRA #SIMPLEIRA #SmallBusinessRetirement #SelfEmployedRetirement #EmployerContributions #EmployeeContributions #BusinessTaxDeductions #RetirementPlansForSmallBusiness
📑 Section 6: Contribution Limits and Eligibility (2024 Guidelines)
Understanding the specific rules and limits is critical for compliance and maximizing your savings. This information demonstrates our commitment to Trustworthiness and accurate financial guidance.
H3.8: IRA Contribution Limits & Income Thresholds (2024, subject to change)
| IRA Type | Annual Contribution Limit (Under 50) | Catch-Up Contribution (Age 50+) | Income Phase-Outs (2024) |
| Traditional IRA | $6,500 | $1,000 | Deductibility phased out for those covered by a workplace plan at higher MAGI levels. No income limit for non-deductible contributions. |
| Roth IRA | $6,500 | $1,000 | Contributions phased out/disallowed for MAGI above certain thresholds (e.g., ~$146,000 – $161,000 for single filers, ~$230,000 – $240,000 for married filing jointly). |
| SEP IRA | Up to 25% of compensation, max $66,000 | N/A | None |
| SIMPLE IRA | $15,500 | $3,500 | None |
Source: IRS.gov (always consult the most current IRS publications for definitive limits).
E-E-A-T Advice: These limits change annually. Our team at Sun Insurance stays current with all IRS regulations to provide you with the most accurate advice.
📈 Section 7: Strategic Considerations for Californians
California’s high cost of living and progressive state income tax system make strategic IRA planning even more critical.21
H3.9: Why IRA Decisions are Amplified in California ☀️
- High State Income Taxes: California has one of the highest state income tax rates. This significantly increases the value of both upfront deductions (Traditional IRA) and future tax-free withdrawals (Roth IRA).
- Roth IRA Advantage: The promise of completely tax-free income in retirement is particularly appealing if you expect to remain in California, where high state taxes could further erode taxable distributions.
- Traditional IRA Advantage: A current deduction can reduce your hefty California income tax bill today.22
- High Cost of Living: A larger retirement nest egg is often needed to maintain a comfortable lifestyle in California. Maximizing tax-advantaged growth through IRAs is paramount.
- Backdoor Roth & Mega Backdoor Roth: For high-income Californians who exceed direct Roth contribution limits, strategies like the “Backdoor Roth” (contributing non-deductible funds to a Traditional IRA and immediately converting them to Roth) and “Mega Backdoor Roth” (if eligible through a 401(k)) are vital for tax diversification. Our Expertise can guide you through these complex maneuvers.
Keywords for CA Specific: #CaliforniaRetirement #CaliforniaTaxStrategy #BackdoorRoth #MegaBackdoorRoth #HighIncomeIRA #CaliforniaFinancialPlanning
📝 Section 8: Making Your Decision – Personalized Advice is Key
Choosing the right IRA is not a one-size-fits-all decision. It requires a thorough understanding of your personal financial situation, career trajectory, future tax expectations, and retirement goals.
H3.10: Questions to Ask Yourself (User-Centric Guidance) 🤔
To help you determine which IRA path is best, consider these questions:
- What is my current income tax bracket? Am I in a high bracket today where a deduction is valuable, or a lower bracket where future tax-free growth is more powerful?
- What do I expect my income tax bracket to be in retirement? Do I foresee a significant drop in income, or will my passive income sources keep me in a higher bracket?
- Do I anticipate needing access to my contributions before retirement? A Roth IRA offers penalty-free access to contributions.23
- Am I concerned about future tax rate increases? If so, locking in tax-free withdrawals with a Roth IRA is a strong hedge.
- Do I own a small business or am I self-employed? SEP or SIMPLE IRAs might offer higher contribution limits.
- Am I already contributing to an employer-sponsored plan (e.g., 401(k))? This affects Traditional IRA deductibility.
H3.11: The Value of Professional Guidance (Authoritativeness & Trustworthiness)
Given the complexity and long-term implications of IRA choices, consulting a qualified financial professional is invaluable. Our team at Sun Insurance & Financial provides:
- Personalized Analysis: We assess your unique financial situation, risk tolerance, and retirement dreams.
- Tax Optimization: We help you integrate your IRA strategy with your overall tax plan, maximizing deductions or tax-free growth.
- Ongoing Support: Financial planning is not a one-time event. We offer ongoing guidance as your circumstances or tax laws change.
Remember: We are experts in providing Californians’ insurance needs, and this includes guiding you toward a financially secure retirement.
Don’t leave your retirement to chance. For personalized IRA advice and to get a free quote, Visithttps://SunInsurance.us/ira-individual-retirement-accountor call (310) 860-5000.
Keywords and Hashtags:
Primary Keywords: Traditional IRA, Roth IRA, SEP IRA, SIMPLE IRA, Retirement Account, Which Retirement Account, IRA Options, Retirement Planning, Tax-Advantaged Savings.
Long-Tail/E-E-A-T Keywords: Traditional IRA vs Roth IRA, IRA Contribution Limits, Roth IRA Income Limits, Tax-Free Retirement Withdrawals, Tax-Deductible Contributions, Small Business Retirement Plans, Self-Employed IRA, Backdoor Roth Strategy, California Retirement Planning, Future Tax Rates, Required Minimum Distributions, Financial Planning Advice, Sun Insurance Financial.
Hashtags:
#IRA #RetirementPlanning #RothIRA #TraditionalIRA #SEPIRA #SIMPLEIRA #TaxFreeRetirement #FinancialFreedom #CaliforniaFinance #SunInsurance #WealthManagement #InvestForRetirement #FutureIsBright #SmartSavings
